MGT 300 CHAPTER 12 : ENTERPRISE RESOURCES PLANNING
LEARNING OUTCOMES :
- Describe the role information plays in enterprise resources planning systems
- Identify the primary forces driving the explosive growth of enterprise resources planning systems
- Explain the business value of integrating supply chain management, customer relationship management, and enterprise resources planning systems
- ENTERPRISE RESOURCES PLANNING (ERP)
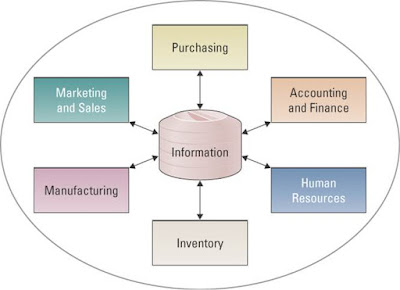
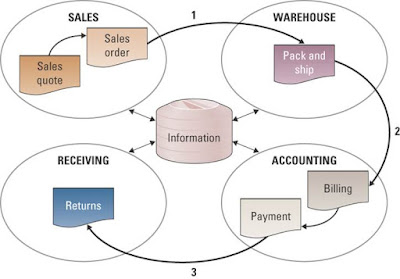
-At the heart of all ERP systems is a databases when a user enters or updates information in one module, it is immediately and automatically updated throughout the entire system

-ERP systems automate business processes

- BRINGING THE ORGANIZATION TOGETHER
-Organization before ERP

-In most organization, information has traditionally been isolated within specific departments, whether on an individual databases, in a file cabinet or on an employee's PC.
*DISADVANTAGES :
-updates issues
-redundancy
-inaccurate information across databases
-different formats of information in the different databases
- bringing the organization together

-ERP enables employees across the organization to share information across a single and centralized databases.
*DISADVANTAGES :
-not as flexible and far more difficult to change
-might not meet all department needs as well as an individual specific system
-multiple access levels increases security issues
-ethical dilemmas from accessing different department information such as payroll
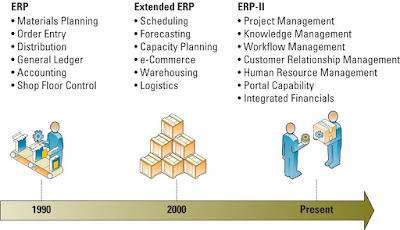
- THE EVOLUTION OF ERP

- INTEGRATING SCM, CRM, and ERP
-SCM, CRM, and ERP are the backbone of e-business
-Integration of these applications is the key to success for many companies
-Integration allows the unlocking of information to make it available to any user, anywhere, and anytime
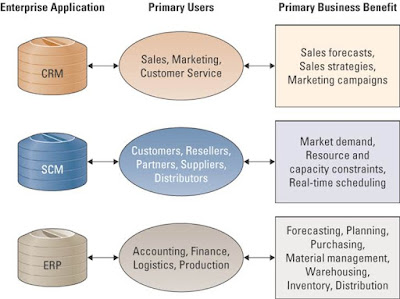
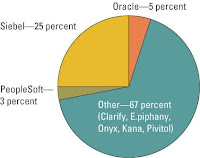
*SCM and CRM market overviews
-General audience and purpose of of SCM, CRM, and ERP

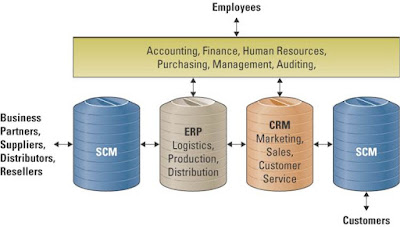
- INTEGRATION TOOLS
-Data points where SCM, CRM and ERP integrate

-ERP systems must have integrate various organization processes and be :
*Flexible :
-must be able to quickly respond to the changing needs of the organization
*Modular and open ;
-must have an open system architecture, meaning that any module can be interface with or detached whenever required without affecting the other modules
*Comprehensive :
- must be able to supports a variety of organizational functions for a wide range of businesses
*Beyond the company :
-must support external partnerships and collaborations efforts





Enterprise Resource Planning is crucial for business efficiency! With atmosphereswitch, you can ensure your ERP systems are hosted securely and run smoothly for optimal performance.
ReplyDelete