MGT 300 CHAPTER 15 : OUTSOURCING IN THE 21st CENTURY

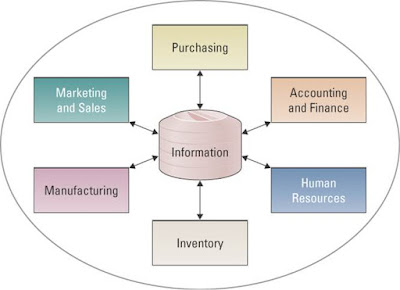
LEARNING OUTCOMES : Describe the advantages and disadvantages of insourcing, outsourcing, and offshore outsourcing. Describe why outsourcing is a critical business decision. OUTSOURCING PROJECTS -Insourcing (in-house-development) : is a common approach using the professional expertise within an organization's information technology system -Outsourcing : is an arrangement by which one organization provides a service or services for another organization that chooses not perform them in house *Reasons companies outsource * 3 TYPES OF OUTSOURCING Onshore outsourcing : engaging another company within the same country for services Nearshore outsourcing : contracting an outsourcing arrangement with a company in a nearby country Offshore outsourcing : using organization from developing countries to write code and develop systems *Big selling point for offshore outsourcing 'inexpensive good work'. ...